NRST Spiro-Torq

Background
Date : April 2019 Location : Mediterranean Sea
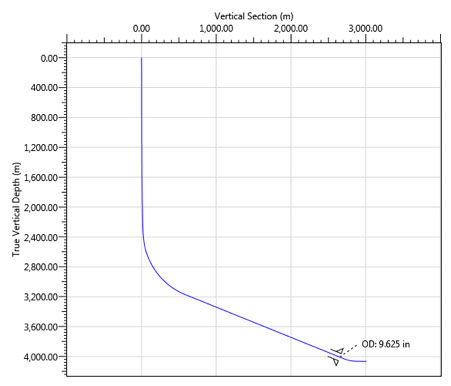
The operator was concerned with high rotary torques while drilling highly deviated development wells (Plot 1 for well profile). The wells were to be being drilled from an ultra- deepwater drillship which had extremely high costs. Any measure which could protect the wellbore and improve drilling efficiency was to be commended.
Equipment
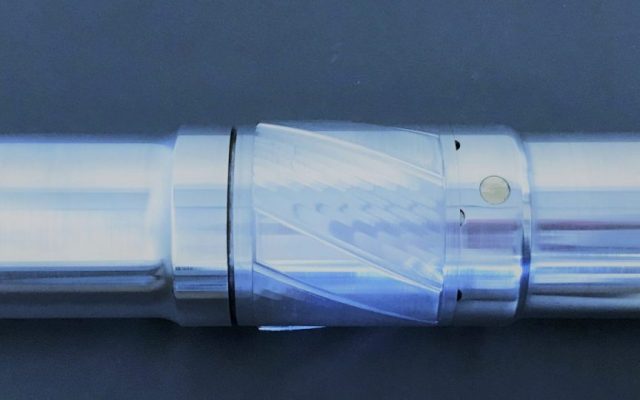
The NRST Spiro-Torq® tools were selected to assist with reducing torque and to enhance drilling efficiency. The operator ran both 6 5/8 FH and NC50 drillstring, all which were range 3, and in varying configurations. The 6 5/8 FH and NC50 Spiro-Torq® tools have 10″ OD and 8.10″ OD sleeves respectively, which provide excellent tool joint standoff.
For ease of satisfying contractual terms and conditions, the tools were supplied through a third-party service organisation. We have very good relationships with many drilling contractors and larger service companies, which helps simplify logistics and paperwork, and above all saves time.
Operations
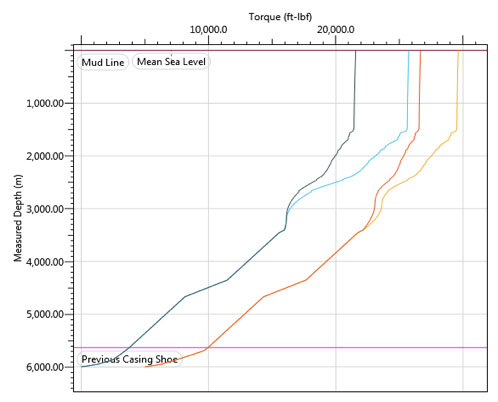
The NRST Spiro-Torq® tools were run in both the 12 1/4” and 8 1/2” sections, placed at one tool every stand (42m) of drill pipe. A torque and drag analysis was performed using the latest version of Landmark’s Wellplan software (Plot 2) and our engineers provided specific tool placement recommendations. All tools were run by the rig crew as we typically do not need to send any Drilltech personnel to the rig, and this has a saving on cost, rig space, logistics, and other personnel support activities.
Results
The rotary torque was significantly reduced, and closely matched the computer model predictions.
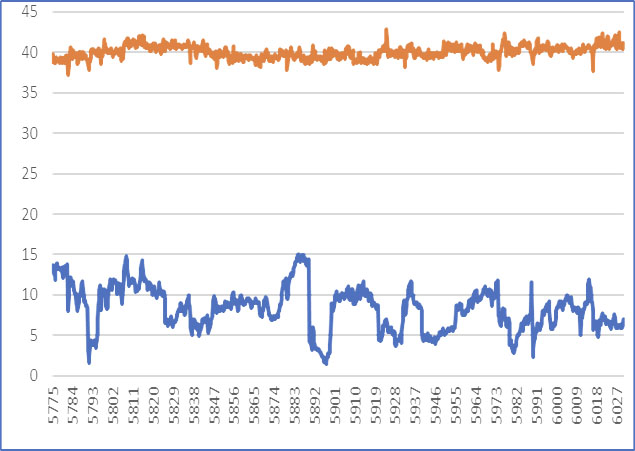
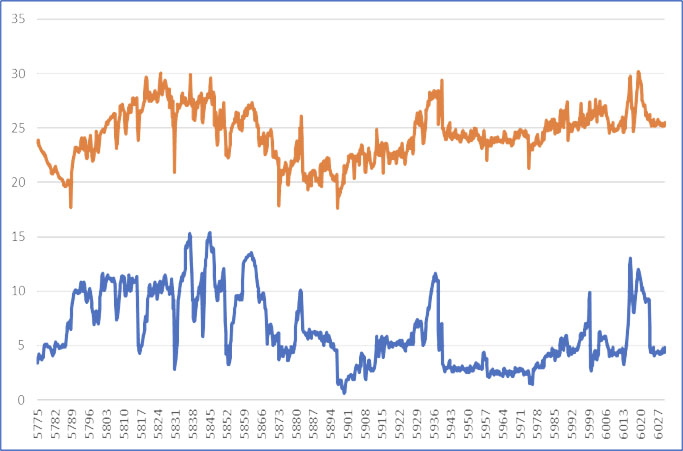
The rate of penetration (ROP), as compared to a prior well drilled in the same formation and with a similar well profile but without NRST Spiro-Torq® tools, improved dramatically. Plot 3 and 4 below demonstrate the difference in torque behaviour by changing the WOB.
On Well A, without NRST Spiro-Torq® tools, the torque value did not follow changes in WOB, as presumably there was poor transfer of energy to the bit. However, on Well B with the NRST Spiro-Torq® tools, torque tracked the WOB quite markedly.
Lessons Learnt
By running NRST Spiro-Torq® tools to provide a standoff of the drill string from the wellbore ID, not only can we influence and reduce torque generated across high sideload zones, and reduce casing wear at the same time, we might also improve weight transfer to the bit. This may assist in improving ROP and thus saving valuable rig time.